Games and AI: How Generative Models Are Transforming Game Worlds and Characters
In 2025, artificial intelligence has become an integral part of the gaming industry, influencing everything from character creation to dynamic storytelling. Generative models such as GPT and DALL·E are no longer just tools for text or image generation — they are active contributors to the way developers craft virtual experiences, shaping the future of digital entertainment.
The Role of Generative AI in Game Design
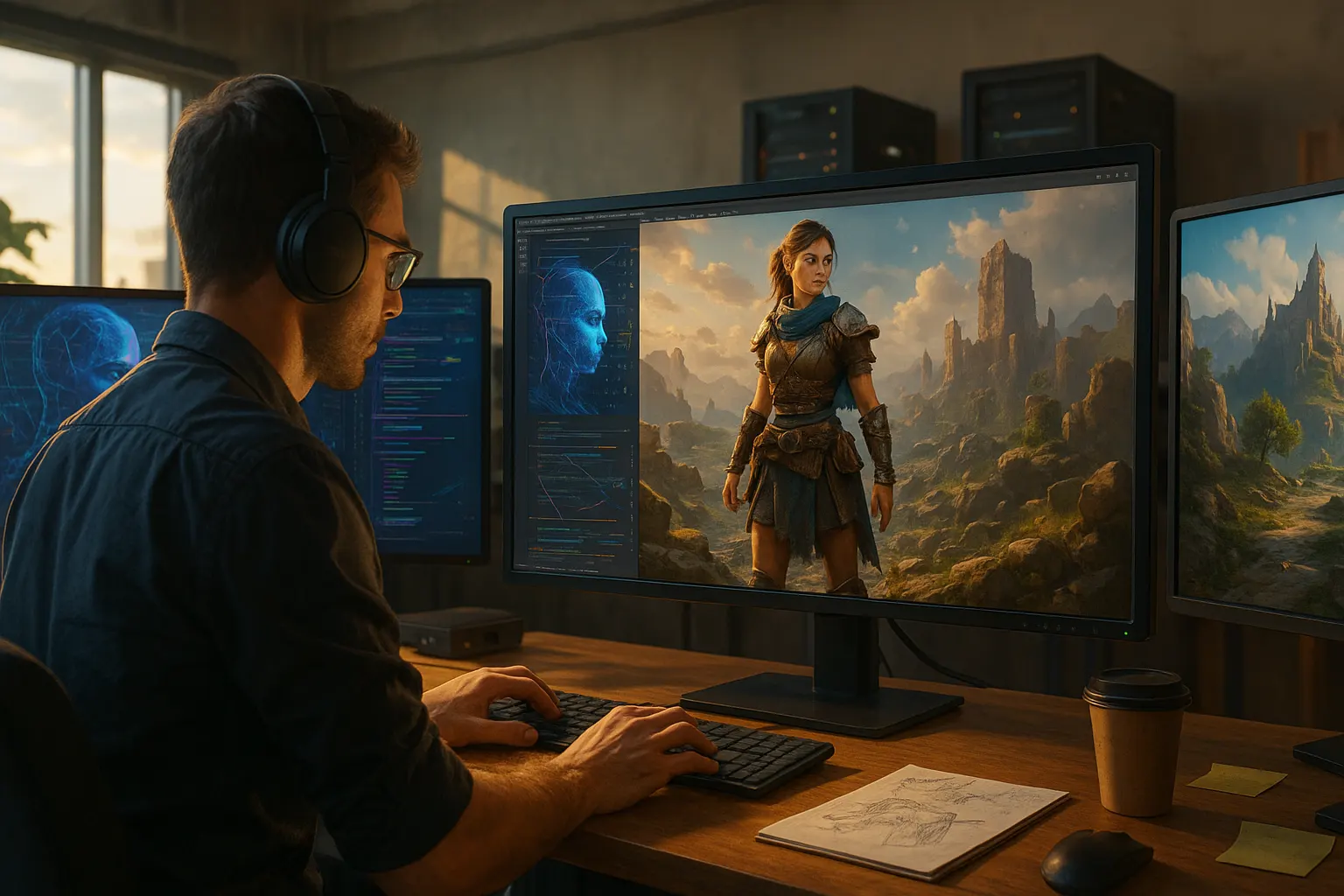
Generative AI has introduced a new era of creativity in game development. Through models like GPT-5 or Stable Diffusion, designers can instantly generate dialogue, environments, and missions that feel organic and unpredictable. This dynamic generation allows for games to become more immersive and responsive to player choices, providing unique experiences for each user.
Modern engines now integrate AI-assisted tools capable of producing textures, architectural elements, and lighting that adjust in real time. Developers save hundreds of hours that were previously spent on repetitive design tasks, redirecting their efforts toward refining gameplay and narrative depth. The combination of human vision and machine creativity forms a synergy that was once unimaginable.
Studios like Ubisoft, Electronic Arts, and CD Projekt Red are actively testing in-house AI systems that generate adaptive side quests or emotional dialogue responses. This trend points to a future where each player’s version of a game world evolves differently — guided by generative intelligence rather than pre-scripted events.
Procedural Storytelling and Character Depth
One of the most fascinating applications of generative AI is in narrative development. Instead of relying on fixed dialogue trees, AI-driven systems can craft conversations that reflect a player’s tone, past actions, and moral decisions. Characters no longer behave as static entities but evolve as living participants within the game’s universe.
AI models like ChatGPT and Gemini are trained on storytelling datasets that include literary styles, cinematic dialogues, and even emotional context. This allows them to produce believable reactions and evolving relationships between non-playable characters (NPCs) and players. As a result, games become emotionally richer and more human in their interactions.
Furthermore, generative AI can adapt plotlines in real time, introducing unexpected twists based on player data. For instance, an AI might modify a quest’s outcome depending on previous moral decisions or combat styles, ensuring that no two playthroughs are ever identical.
Visual Design and AI Art Generation
The visual aspect of gaming has experienced a dramatic transformation thanks to image-generation tools. Platforms like Midjourney and DALL·E 3 have empowered artists to create concept art, character models, and entire worlds from simple text prompts. These tools not only accelerate production but also enable indie developers with limited budgets to achieve AAA-level aesthetics.
AI-generated assets are now part of major production pipelines. They help designers prototype environments and costumes in minutes rather than days. For example, Bethesda and Square Enix are experimenting with hybrid pipelines, combining manual artistry with AI image refinement to maintain a distinct visual identity while reducing costs.
However, the rise of AI art in gaming also raises ethical questions about originality and ownership. Developers must balance efficiency with transparency, ensuring that AI-generated visuals respect intellectual property laws and align with artistic integrity.
From Concept to Playable Worlds
AI-generated visuals are no longer static references; they evolve into playable assets. With procedural world-building algorithms, a designer can generate vast, explorable terrains using AI input alone. These worlds adjust to player behaviour, weather patterns, and in-game events — creating a sense of realism beyond manual design limits.
Machine learning tools analyse gameplay data to understand which environments players engage with most. The AI then replicates similar structures or landscapes, creating endless variations without human repetition. This process ensures freshness across long gaming sessions and supports massive open-world projects without proportionally expanding development teams.
By combining AI art generation with physics simulations and spatial computing, developers now build entire cities and ecosystems procedurally. The result is a living, breathing digital universe that reacts to both code and creativity.
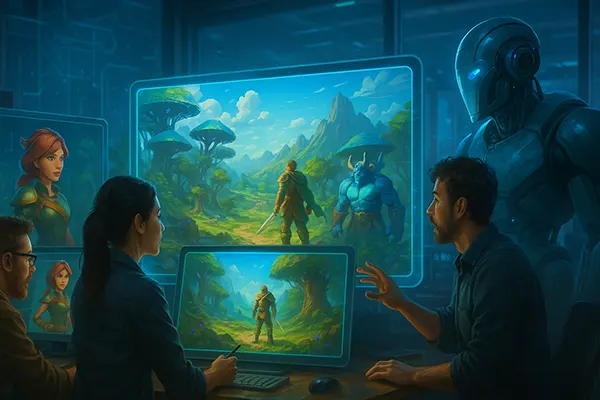

The Future of AI-Driven Game Worlds
As AI continues to evolve, the boundary between developer and machine collaborator becomes increasingly blurred. Future games may rely on persistent AI directors that generate missions, manage NPCs, and even evolve the rules of the world over time. This self-adapting environment creates a deeply personalised gaming experience for each player.
Yet, along with innovation come potential challenges. Developers must address biases within generative models, ensure data privacy, and maintain human oversight in creative decisions. The risk of homogenised design and overreliance on automation could undermine the artistic diversity that defines gaming culture.
Nevertheless, the future looks promising. As technology matures, AI will not replace game designers but rather empower them. It will become a creative partner — one that helps transform imagination into interactive worlds faster and more intuitively than ever before.
Ethical and Creative Balance
The integration of AI into game development requires responsible governance. Studios are already establishing ethical guidelines for AI usage, including crediting AI-generated content and verifying originality. Transparency is essential to maintain trust among players and creators alike.
At the same time, creative experimentation is flourishing. AI offers new perspectives on artistic collaboration, blending computational precision with human storytelling. The challenge lies in using it as a tool for inspiration rather than replacement.
By 2030, experts predict that generative AI will become a foundational element of the global gaming ecosystem. Those who learn to harness its power responsibly today will shape the landscapes of tomorrow’s most unforgettable virtual experiences.